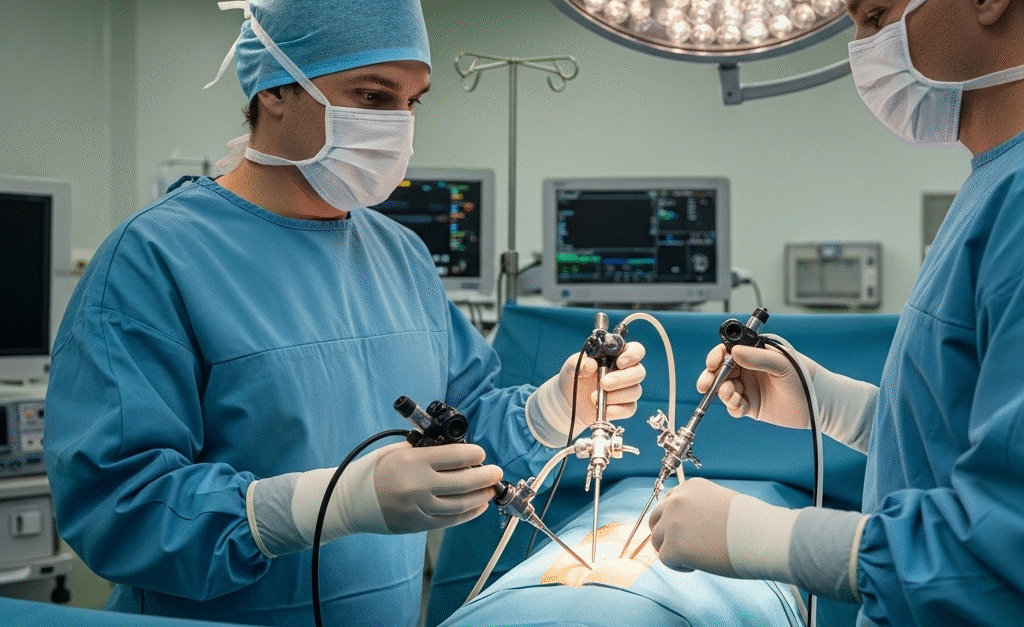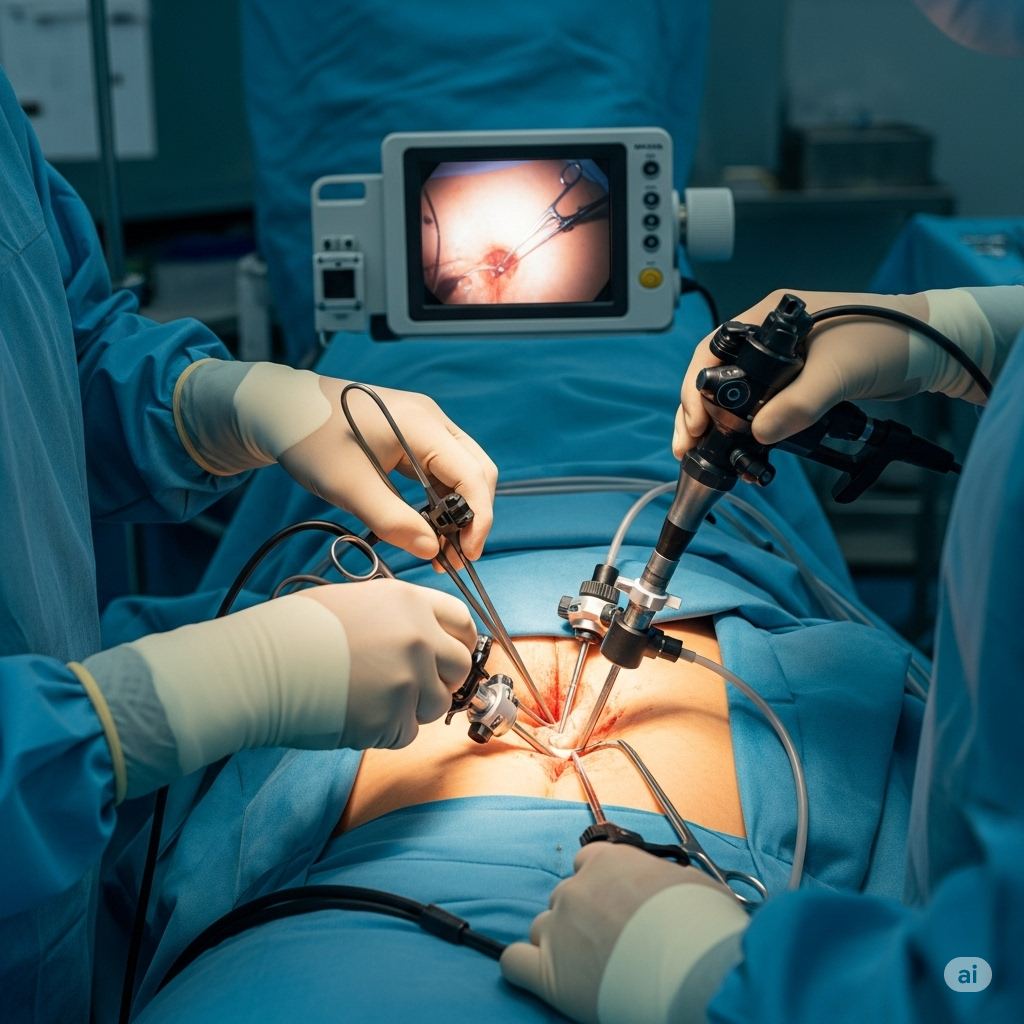
Laparoscopic Procedures
Laparoscopy, often referred to as “keyhole surgery” or minimally invasive surgery, involves making one or more small incisions (typically 0.5-1.5 cm) in the abdomen or pelvis. A laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube with a camera) is inserted through one incision, and specialized surgical instruments are inserted through other small incisions to perform surgical procedures. This technique offers benefits like smaller scars, less pain, and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
Common Laparoscopic Procedures:
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Removal of the gallbladder, typically for gallstones.
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy: Removal of the appendix, commonly for appendicitis.
- Laparoscopic Hernia Repair: Repair of various types of hernias (e.g., inguinal, umbilical, incisional).
- Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus.
- Laparoscopic Myomectomy: Removal of uterine fibroids while preserving the uterus.
- Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy / Oophorectomy: Removal of ovarian cysts or the ovaries.
- Laparoscopic Colectomy: Removal of part or all of the colon, for conditions like diverticulitis, colon cancer, or inflammatory bowel disease.
- Laparoscopic Fundoplication (e.g., Nissen Fundoplication): Surgery to treat severe acid reflux (GERD) by wrapping part of the stomach around the esophagus.
- Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass / Sleeve Gastrectomy: Weight-loss surgeries.
- Diagnostic Laparoscopy: Used to investigate abdominal or pelvic pain, identify causes of infertility, or stage certain cancers, by visually inspecting organs and taking biopsies.
- Laparoscopic Ectopic Pregnancy Removal: Removal of a pregnancy implanted outside the uterus.
- Laparoscopic Endometriosis Surgery: Diagnosis and treatment (removal) of endometrial tissue growing outside the uterus.